04 Apr OCT scan
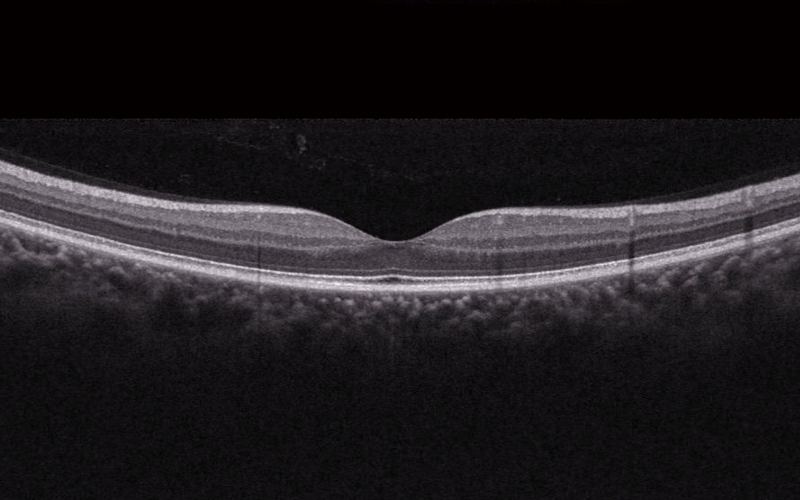
An Optical Coherence Tomography scan (commonly referred to as an OCT scan) is the latest advancement in imaging technology. This diagnostic technique employs light rays to achieve high resolution pictures of the structural layers of the back of the eye, mainly the retina and the optic nerve.
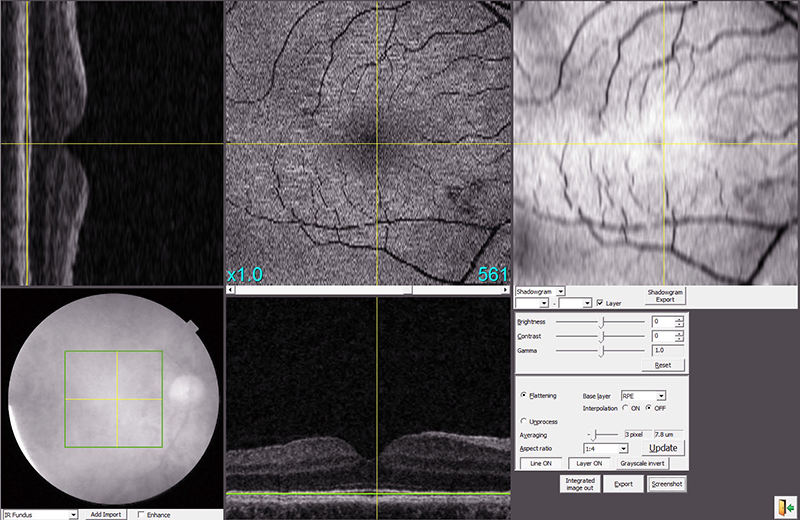
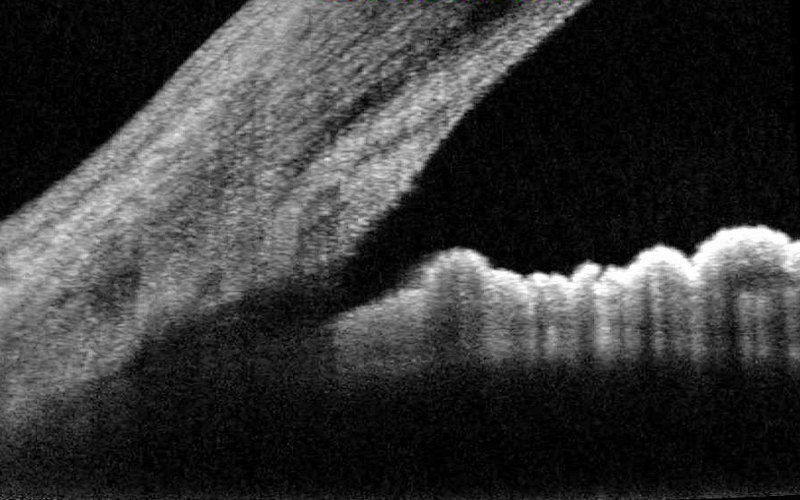
An OCT scan provides color-coded, cross-sectional images of the retina. The thickness and structure of various layers can be measured which helps with the diagnosis.
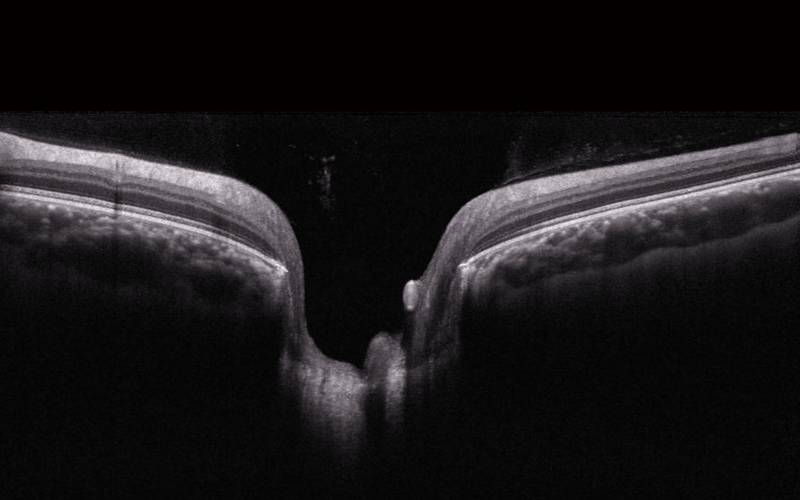
These detailed images are revolutionizing early detection and treatment of eye conditions like age-related macular degeneration, Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy.
An OCT scan is a noninvasive, painless test. It is performed in just about 5-10 minutes right in the clinic itself. Dilating eye drops may need to be put in the eyes prior to the test.
The head is placed on the OCT machine on a support to keep it motionless. The equipment then scans the eye without touching it. Each scan takes less than 3 seconds. Once your eyes are dilated, they may be sensitive to light for a few hours after the exam.
Since OCT relies on light waves, it may not be possible to perform the scan with conditions that interfere with light passing through the eye (like dense cataracts or significant bleeding in the vitreous).


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.