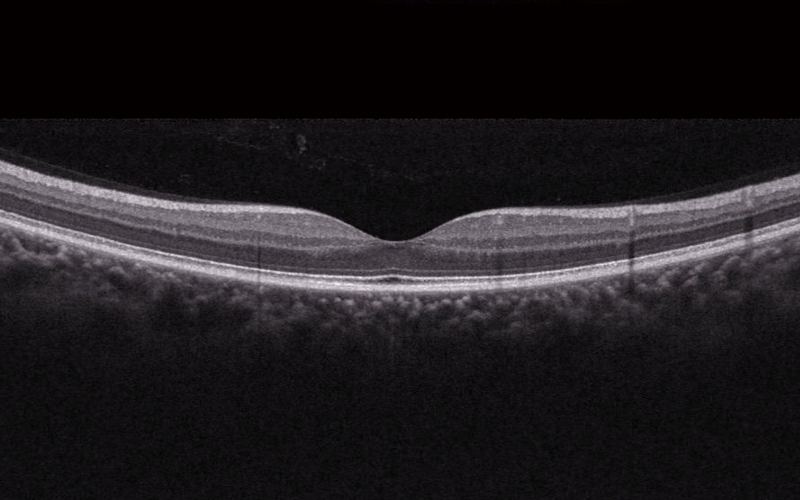
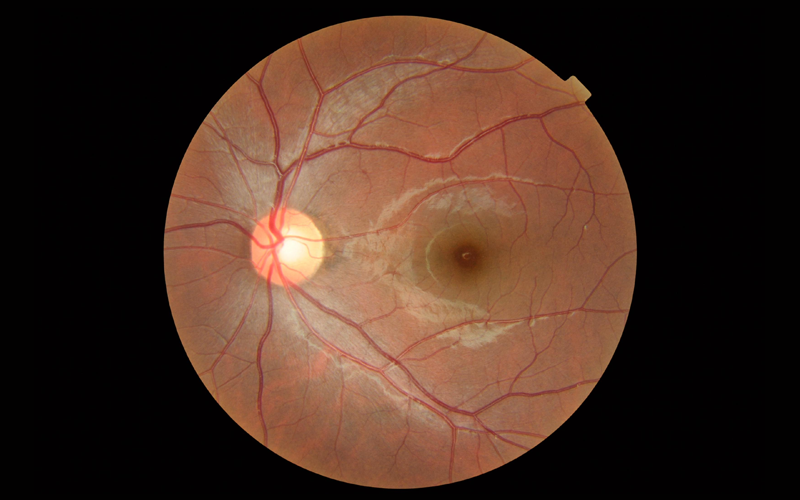
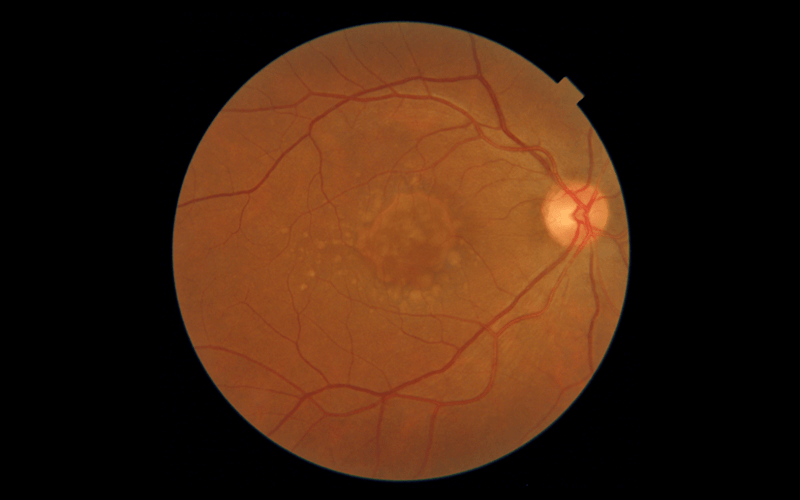
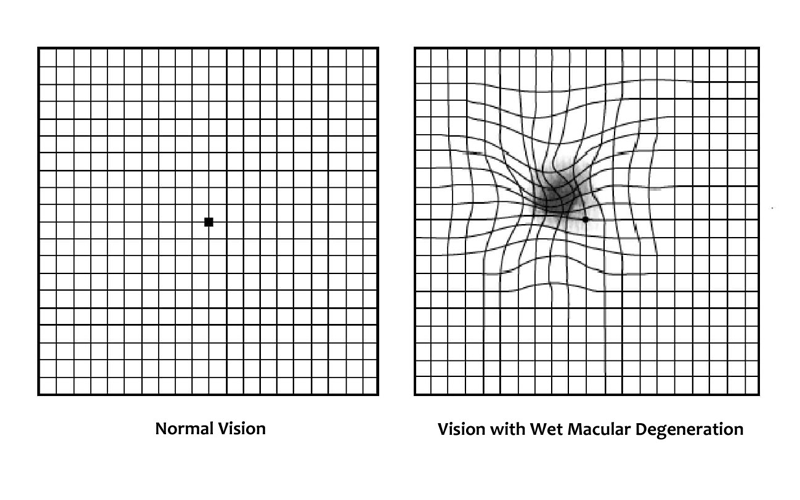
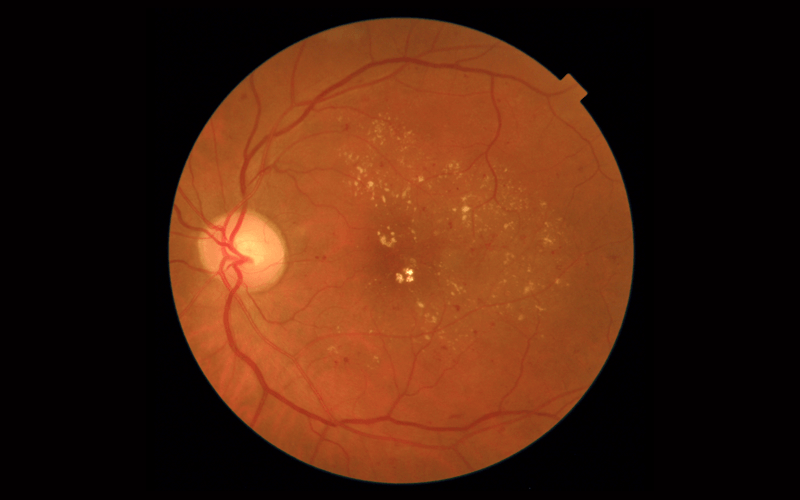
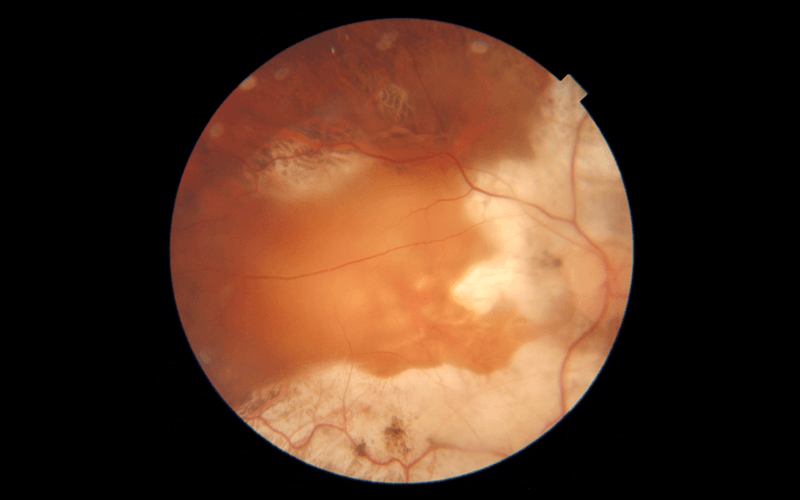
23 Apr Low Vision Rehabilitation and Low Vision Aids
Those with low vision are incapable of performing their routine activities. However that does not mean giving up the activities, but it does mean applying new ways of doing them. Instead of taking over their tasks, they need to be offered adjustments they need to...